
The Link Between Anxiety and Depression: How to Recognize Both
Anxiety and depression are two of the most common mental health conditions worldwide. They affect millions of people every year. Although the symptoms of each are a little different, they share a close relationship. Indeed, it is not at all rare for a person to suffer from both at the same time. It’s important to understand how these two are related and how the signs of each are identified so as to manage and treat them.
The overlapping nature of anxiety and depression
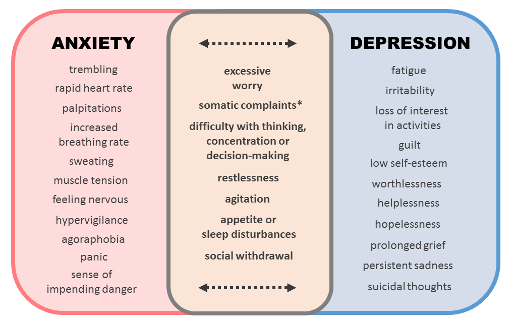
While these are two distinct mental disorders, anxiety and depression share much in common. Anxiety may appear as excessive worry, fear, or nervousness, while depression is characterized by persistent sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest in activities once enjoyed. Often, the boundaries between the two conditions are not sharply defined. Many people experience anxiety as part of depression, and many depressed people experience anxiety.
For instance, a person with GAD will be always on edge and worried about mundane things, which may result in feelings of exhaustion, hopelessness, and sadness. In contrast, depression may manifest as intense sadness that leads to a loss of interest in life, and worries or anxiety about the future may worsen their condition. This can lead to a vicious cycle, where each problem will be worsening the other one and makes it much more challenging to deal with life at hand.
Knowing Signs of Anxiety
There are numerous ways anxiety can appear. Here are some of the most common symptoms:
1.Constant worries: Being in an agitated stateRacing thoughts or an inability to control thoughts, particularly worrisome ones. These include a racing heart, sweating, dizziness, or muscle tension,Restlessness or an inability to relax.
2.Sleep disturbances: Either trouble falling asleep or staying asleep.
3.Avoidance behavior: Where you may avoid certain situations or places due to fear or anxiety.
It is important to note that not all anxiety symptoms are related to specific triggers. Anxiety can be generalized, with worries that seem to pop up without a clear cause, or it can be situation-specific, such as social anxiety or panic attacks.
Recognizing Depression Symptoms
Depression often manifests itself through being overwhelmed by feelings of sadness or hopelessness. It can also manifest physically, emotionally, and cognitively. Some of the most common symptoms are:
1. Recurrent feelings of emptiness, hopelessness, or pervasive and persistent feelings of sadness.
2.Loss of interest or pleasure in activities once considered a source of enjoyment.
3.Fatigue or loss of energy even after rest.
4.Poor ability to concentrate or make decisions.
5.Sleep disturbances: either insomnia or sleeping too much.
6.Recurring thoughts of death or suicide.
Unlike anxiety, depression can feel like emotional numbness, in which everything feels overwhelming or out of reach. If these feelings last for more than two weeks, then that someone is dealing with clinical depression and should seek professional help.
How Anxiety and Depression Often Co-Exist
Relationship between anxiety and depression can be complex, as they mostly occur together, amplifying each other. A person suffering from anxiety may start to feel overwhelmed by the constant state of fear or worry and develop depressive thoughts such as, “I can’t handle this anymore” or “Nothing will ever get better.” Similarly, a person with depression may be so down and hopeless that their natural response is anxiety about their future, relationships, or ability to function.
Research has shown that if one condition is present, the chances of developing the other are increased. Anxiety disorders are among the most common co-occurring conditions for people diagnosed with depression, and the presence of both can have a significant impact on a person’s ability to manage daily life.

What Can You Do About It?
The good news is that both anxiety and depression are treatable. The first step toward recovery is to recognize the symptoms. If you find yourself experiencing both anxiety and depression, seek professional help. A mental health professional can diagnose the conditions and develop a treatment plan tailored to your needs. Treatment options may include:
1. Therapy: Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) is a widely used technique that helps a person identify problematic thought patterns and replace them with healthier, more productive thinking. Other modalities of therapy include talk therapy, exposure therapy, and similar others.
2.Medication: Antidepressants and anxiety medications can be prescribed to help one balance the chemicals in the brain relating to mood and anxiety level.
3.Lifestyle Changes: Regular physical exercise, proper nutrition, and stress management techniques such as mindfulness or meditation can significantly reduce the symptoms of anxiety and depression.
4.Support Networks: Reaching out to friends and family who are supportive or joining a support group is helpful in providing a sense of connection and understanding.
Conclusion
It is very essential for anyone experiencing these conditions to understand the connection between anxiety and depression. Early recognition of the overlapping symptoms and seeking professional help can lead to a better outcome and quality of life. If you, or someone you know is suffering from anxiety, depression, or a combination of both, it is quite okay to ask for help. You are not alone in this fight and with the right treatment, there is hope to manage your symptoms and find relief.
To read more about the following topic, click below:
